By John Canterbury, M.D.
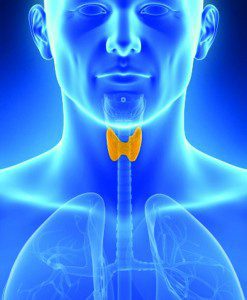 The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland that is located over the trachea (wind pipe) just below the larynx (voice box). The thyroid gland plays a very important role in most all the metabolic processes of the body. The thyroid gland produces a hormone and together the gland and hormone are responsible for regulating metabolism.
The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland that is located over the trachea (wind pipe) just below the larynx (voice box). The thyroid gland plays a very important role in most all the metabolic processes of the body. The thyroid gland produces a hormone and together the gland and hormone are responsible for regulating metabolism.
How Thyroid Hormone is Made
The hypothalamus, often referred to as the body’s “thermostat” is responsible for making sure the thyroid blood levels are normal. When the hypothalamus notices the thyroid blood levels decreasing it releases TRH (thyroid releasing hormone). The TRH then signals the pituitary gland to release TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to begin producing thyroid hormone.
When the body’s levels of thyroid hormone become normal and the body is functioning normally the pituitary gland will cease its release of TSH and the process stops until the hypothalamus notices the thyroid hormone levels decreasing again.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is caused by insufficient production or absorption of thyroid hormone that causes abnormally low blood thyroid hormone levels. This problem with the thyroid gland is usually brought about as a result of iodine insufficiency, a tumor, a damaged thyroid gland, or vitamin deficiencies. This type of hypothyroidism is called primary hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism can also be a result of the pituitary gland and/or hypothalamus failing to function properly. This type of hypothyroidism is called secondary hypothyroidism.
Low thyroid hormone levels may not only make you feel old, they can propel you into the conditions and diseases associated with aging. Low levels of T4 can be responsible for weight gain, since T4 plays a role in controlling the body’s metabolism. The changes that are brought about as a result of the aging process such as changes in the fat to muscle ratio and the shrinkage of organs can also be caused by a lack of thyroid hormone. A decrease in the amount of lean body mass can in turn interfere with the activity of an enzyme that converts thyroxine (T4) into triodothyronine (T3). T3 is about 5 times more potent than T4.
Adequate levels of thyroid hormone are needed to regulate blood sugar, so a deficiency of thyroid hormone can lead to adult-onset diabetes. Low levels of thyroid hormone can also greatly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease due to an increase in the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides and may cause high blood pressure. Also, iodine is essential to the proper functioning of the thyroid gland, several studies that have been done have shown a correlation between low iodine levels and an increased risk of cancer.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism include:
. weakness, fatigue, and lack of energy
. dry, flaky, pale skin
. dry, coarse, dull hair, loss of hair
. lack of appetite
. weight gain
. thinning of eye brows
. sensitivity to cold
. brittle nails
. cold hands and feet
. constipation
. low body temperature
Hypothyroidism is one of the most overlooked conditions in older patients. The general opinion of many in the medical community has been that the drop that occurs in hormone levels is a normal part of the aging process. Thyroid replacement therapy that can alleviate or improve most, if not all the symptoms caused by the thyroid gland.
John Canterbury MD
South Florida Internal Medicine
680 Second Avenue North, Suite 203
Naples, FL 34102
239-330-1382