Nutrition and physical activity are important parts of a healthy lifestyle when you have diabetes. Along with other benefits, following a healthy meal plan and being active can help you keep your blood glucose level in your target range. To manage your blood glucose, you need to balance what you eat and drink with physical activity and diabetes medication, if you take any. What you choose to eat, how much you eat, and when you eat are all important in keeping your blood glucose level in the range that your health care team recommends.
Nutrition and physical activity are important parts of a healthy lifestyle when you have diabetes. Along with other benefits, following a healthy meal plan and being active can help you keep your blood glucose level in your target range. To manage your blood glucose, you need to balance what you eat and drink with physical activity and diabetes medication, if you take any. What you choose to eat, how much you eat, and when you eat are all important in keeping your blood glucose level in the range that your health care team recommends.
Becoming more active and making changes in what you eat and drink can seem challenging at first. You may find it easier to start with small changes and get help from your family, friends, and health care team. Eating well and being physically active most days of the week can help you: keep your blood glucose level, blood pressure, and cholesterol in your target ranges; lose weight or stay at a healthy weight; prevent or delay problems associated with diabetes; feel good and have more energy.
Food
The key to eating with diabetes is to eat a variety of healthy foods from all food groups, in the amounts your meal plan outlines.
• vegetables
– nonstarchy: includes broccoli, carrots, greens, peppers, and tomatoes
– starchy: includes potatoes, corn, and green peas
• fruits—includes oranges, melon, berries, apples, bananas, and grapes
– grains—(at least half of your grains for the day should be whole grains)includes wheat, rice, oats, cornmeal, barley, and quinoa such as bread, pasta, cereal, and tortillas
• Protein – lean meat, chicken or turkey without the skin, fish, eggs, nuts and peanuts, dried beans and certain peas, such as chickpeas and split peas, meat substitutes, such as tofu
• dairy—nonfat or low fat – milk or lactose-free milk if you have lactose intolerance, yogurt, cheese
Eat foods with heart-healthy fats, which mainly come from these foods: oils that are liquid at room temperature, such as canola and olive oil, nuts and seeds, heart-healthy fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, avocado. Use oils when cooking food instead of butter, cream, shortening, lard, or stick margarine.
Limit – fried foods and other foods high in saturated fat and trans fat, foods high in salt/sodium, sweets, beverages with added sugars. Drink water instead of sweetened beverages. Consider using a sugar substitute in your coffee or tea. If you drink alcohol, drink moderately—no more than one drink a day if you’re a woman or two drinks a day if you’re a man. If you use insulin or diabetes medicines that increase the amount of insulin your body makes, alcohol can make your blood glucose level drop too low. This is especially true if you haven’t eaten in a while. It’s best to eat some food when you drink alcohol.
When should I eat?
Some people with diabetes need to eat at about the same time each day. Others can be more flexible with the timing of their meals. Depending on your diabetes medicines or type of insulin, you may need to eat the same amount of carbohydrates at the same time each day. If you take “mealtime” insulin, your eating schedule can be more flexible.
Weight-loss planning
If you are overweight or have obesity, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan. To lose weight, you need to eat fewer calories and replace less healthy foods with foods lower in calories, fat, and sugar. If you have diabetes, are overweight or obese, and are planning to have a baby, you should try to lose any excess weight before you become pregnant. Learn more about planning for pregnancy if you have diabetes.
Physical Activity
Physical activity lowers blood glucose levels, lowers blood pressure, improves blood flow, burns extra calories, improves your mood, can prevent falls and improve memory in older adults, and may help you sleep better.
Even small amounts of physical activity can help. Experts suggest that you aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity 5 days of the week. Be patient. It may take a few weeks of physical activity before you see changes in your health.
Be sure to drink water before, during, and after exercise to stay well hydrated. The following are some other tips for safe physical activity when you have diabetes.
Prevent low blood glucose
Because physical activity lowers your blood glucose, you should protect yourself against low blood glucose levels, also called hypoglycemia. You are most likely to have hypoglycemia if you take insulin or certain other diabetes medicines, such as a sulfonylurea. Hypoglycemia also can occur after a long intense workout or if you have skipped a meal before being active. Hypoglycemia can happen during or up to 24 hours after physical activity.
Planning is key to preventing hypoglycemia. For instance, if you take insulin, your health care provider might suggest you take less insulin or eat a small snack with carbohydrates before, during, or after physical activity, especially intense activity. You may need to check your blood glucose level before, during, and right after you are physically active.
Stay safe when blood glucose is high
If you have type 1 diabetes, avoid vigorous physical activity when you have ketones in your blood or urine. Ketones are chemicals your body might make when your blood glucose level is too high, a condition called hyperglycemia, and your insulin level is too low. If you are physically active when you have ketones in your blood or urine, your blood glucose level may go even higher. Ask your health care team what level of ketones are dangerous for you and how to test for them. Ketones are uncommon in people with type 2 diabetes.
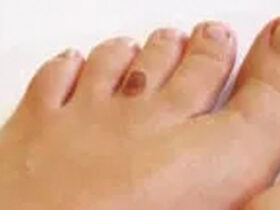
Take care of your feet
People with diabetes may have problems with their feet because of poor blood flow and nerve damage that can result from high blood glucose levels. To help prevent foot problems, you should wear comfortable, supportive shoes and take care of your feet before, during, and after physical activity.
Physical Activity
Doing different types of physical activity each week will give you the most health benefits. Mixing it up also helps reduce boredom and lower your chance of getting hurt. Try these options for physical activity. If you have been inactive or you are trying a new activity, start slowly, with 5 to 10 minutes a day. Then add a little more time each week. Increase daily activity by spending less time in front of a TV or other screen. Try these simple ways to add physical activities in your life each day:
• Walk around while you talk on the phone or during TV commercials.
• Do chores, such as work in the garden, rake leaves, clean the house, or wash the car.
• Park at the far end of the shopping center parking lot and walk to the store.
• Take the stairs instead of the elevator.
• Make your family outings active, such as a family bike ride or a walk in a park.
Aerobic exercise is activity that makes your heart beat faster and makes you breathe harder. You should aim for doing aerobic exercise for 30 minutes a day most days of the week. You do not have to do all the activity at one time. You can split up these minutes into a few times throughout the day.
To get the most out of your activity, exercise at a moderate to vigorous level. Try walking briskly or hiking, climbing stairs, swimming or a water-aerobics class, dancing, riding a bicycle or a stationary bicycle, taking an exercise class, playing basketball, tennis, or other sports.
Strength training is a light or moderate physical activity that builds muscle and helps keep your bones healthy. Strength training is important for both men and women. When you have more muscle and less body fat, you’ll burn more calories. Burning more calories can help you lose and keep off extra weight.
You can do strength training with hand weights, elastic bands, or weight machines. Try to do strength training two to three times a week. Start with a light weight. Slowly increase the size of your weights as your muscles become stronger.
Stretching exercises are light or moderate physical activity. When you stretch, you increase your flexibility, lower your stress, and help prevent sore muscles. You can choose from many types of stretching exercises. Yoga is a type of stretching that focuses on your breathing and helps you relax. Even if you have problems moving or balancing, certain types of yoga can help.
Disclaimer: This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.