By Amanda Tezyk, APRN, BSN, RN
 When metals like lead, mercury, iron, and arsenic build up in your body, they can be toxic. Chelation therapy is a treatment that uses medicine to remove these metals so they don’t make you sick. Chelation therapy uses special drugs that bind to metals in your blood. You get the chelating medicine through an intravenous (IV) tube. Once the drug has attached to the metal, your body removes them both through your urine.
When metals like lead, mercury, iron, and arsenic build up in your body, they can be toxic. Chelation therapy is a treatment that uses medicine to remove these metals so they don’t make you sick. Chelation therapy uses special drugs that bind to metals in your blood. You get the chelating medicine through an intravenous (IV) tube. Once the drug has attached to the metal, your body removes them both through your urine.
Chelation therapy has been around for over 60 years. The medical industry prefers not to recognize a simple over-the-counter procedure that can prevent unnecessary surgery and suffering. Heart disease is a very big and profitable business. It’s easier to pay the overhead on a large medical facility when the operating rooms are constantly filled with heart patients.
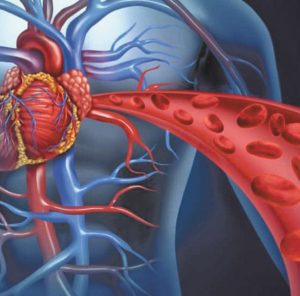
Chelation therapy as practiced in Florida has been proven to increase blood flow and remove plaque build-up in the arteries. Chelation therapy is a safe and effective method of eliminating scale or plaque, which is the primary cause of cardiovascular disease. Other benefits of chelation therapy are the reversal of arteriosclerosis, prevention of heart attacks and strokes, and eliminates the need for bypass surgery and angioplasty.
Chelation comes from the Greek word chele meaning “to claw” or “to bind”. The use of chelation therapy goes back to the 1950s when it was found to be effective in the removal of lead. Studies published in reputable medical and scientific journals have repeatedly confirmed the effectiveness of I V (intravenous) chelation therapy. Over five hundred thousand patients in the United States during the last 40 years have used chelation therapy safely. Even though the FDA has not approved chelation therapy for cardiovascular problems over 1000 physicians recommend and administer chelation.
EDTA chelation therapy might directly remove calcium found in fatty plaques that block arteries, thus breaking up the plaques. Chelation therapy may stimulate the release of a hormone that in turn causes calcium to be removed from plaques or causes a lowering of cholesterol levels. Chelation therapy may reduce the damaging effects of oxygen ions (oxidative stress) on the walls of the blood vessels, which could reduce inflammation in the arteries and improve blood vessel function.
Despite the lack of scientific proof that chelation therapy can effectively treat problems other than proven heavy metal poisoning, the 2007 National Health Interview Survey, conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, found that 111,000 adults 18 years of age and older used chelation therapy as a form of complementary or alternative medicine in the previous 12 months.
The National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, both arms of the National Institutes of Health, are completing a five-year study of chelation therapy as a treatment for heart disease. The protocol for the trial is used worldwide by chelation therapy practitioners; it is being used in the study to ensure that the most widely practiced method of delivering EDTA chelation therapy is rigorously tested. In the study, EDTA chelation therapy or a placebo solution is delivered through intravenous infusions administered over a 28-month course of treatment. The first 30 infusions are delivered every week and the last 10 are delivered bimonthly. In announcing the study, NCCAM noted that EDTA chelation therapy as practiced today often includes the administration of high doses of antioxidant vitamin and mineral supplements and suggested that any positive effects of the therapy might be due to these supplements.
The most common side effect of chelation therapy is a burning sensation at the site where the EDTA is injected into the vein. Rarely, side effects can include fever, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Serious and potentially fatal side effects, which are very rare, include heart failure; a sudden drop in blood pressure; abnormally low blood levels of calcium; permanent kidney damage; and bone marrow depression (meaning that blood cell counts fall). Infrequently, reversible kidney injury has been reported. Other serious side effects can occur if EDTA is not administered by a trained health professional.
The American Board of Clinical Metal Toxicology (originally the American Board of Chelation Therapy) establishes qualifications for practitioners who wish to be trained in chelation therapy, authorizes and approves training seminars, and administers examinations for board certification, and grants board certification to qualified applicants. In addition, the American College for Advancement in Medicine offers a training course in chelation therapy and certification for physicians, naturopathic doctors, and nurse practitioners who have completed the course and passed a qualifying examination.
BR Rejuvenation and Hydration Therapy
239-980-4739
brrejuvenationandhydration.com
brrejuvenationandhydration@gmail.com