 WHAT IS PAIN?
WHAT IS PAIN?
Pain indicates tissue damage. In case of joint pain, the tissue that is damaged is “white” tissue. White tissue refers to joint structures with poor blood supply. Due to the limited blood supply, these structures have a compromised healing ability. White joint structures include cartilage, discs, labrum, ligaments, meniscus, and tendons. Conversely, muscles are red tissue. They have a great blood supply and repair easily.
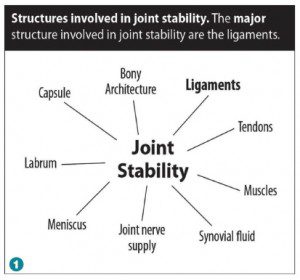
While many structures work together to stabilize the joint, ligaments are the integral stabilizing components. They also act as sensory organs, capable of generating pain. (See Figure 1.) When a ligament is injured, the harmony between the white tissue, muscles, and bony structures is disrupted, interfering with mobility and joint stability.
T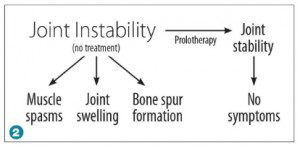 he resultant joint instability then conveys abnormal forces throughout the joint, causing damage to other structures in and around the joint. When the ligaments are left untreated, the body will try to stabilize the joint by causing chronic muscle spasms, joint swelling and eventually bone spur formation and degenerative arthritis … a cycle of chronic pain. (See Figure 2.) Ligament injury to the knee, for example, may give rise to osteoarthritis, runner’s knee, iliotibial band syndrome, chondromalacia patella, meniscus tears, and more.
he resultant joint instability then conveys abnormal forces throughout the joint, causing damage to other structures in and around the joint. When the ligaments are left untreated, the body will try to stabilize the joint by causing chronic muscle spasms, joint swelling and eventually bone spur formation and degenerative arthritis … a cycle of chronic pain. (See Figure 2.) Ligament injury to the knee, for example, may give rise to osteoarthritis, runner’s knee, iliotibial band syndrome, chondromalacia patella, meniscus tears, and more.
CORTISONE SHOTS AND NSAIDS EXACERBATE LONG TERM JOINT DAMAGE
Joint pain and sports injuries are often treated with cortisone, which may temporarily reduce the pain and inflammation in order to get an athlete back in the game right away. But what happens when you turn off the pain signal while the joint is still injured? The individual continues to work, play and remain active on an injured joint, causing further damage! Cortisone is degenerative and promotes weakening of the joint, among other known long term damaging effects.
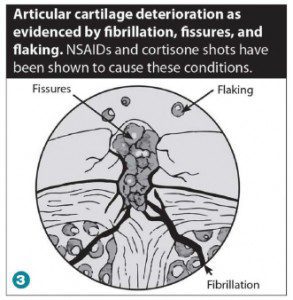 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) are another common treatment for quick, temporary pain relief. NSAID use inhibits the body’s repair processes, leading to decreased proteoglycan and extracellular matrix content and function, which ultimately leads to articular cartilage breakdown. In other words, taking NSAIDs inhibits tissue repair and advances osteoarthritis. Cortisone injections and NSAIDs both cause fibrillation, fissures and flaking of the articular cartilage, which is evidence of cartilage break down.(See Figure 3.)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) are another common treatment for quick, temporary pain relief. NSAID use inhibits the body’s repair processes, leading to decreased proteoglycan and extracellular matrix content and function, which ultimately leads to articular cartilage breakdown. In other words, taking NSAIDs inhibits tissue repair and advances osteoarthritis. Cortisone injections and NSAIDs both cause fibrillation, fissures and flaking of the articular cartilage, which is evidence of cartilage break down.(See Figure 3.)
USING ICE FOR AN INJURY IS OUTDATED
Rest, ice, compression and elevation (RICE) have long been used in the treatment of painful joint injuries. These have now been shown to do more harm than good. Rest and immobilization of the afflicted joint have detrimental effects on the healing ability of ligaments. These modalities inhibit inflammation, which is the natural way by which the body heals post-injury. RICE restricts blood flow to the already blood-poor “white” tissue structures.
Motion, on the other hand, causes an increase of blood flow to the afflicted joint, providing the damaged ligament tissue with nutrients and metabolites necessary for tissue repair and healing. If RICE is out, how can healing be enhanced? MEAT -Movement, Exercise, Analgesics, and Treatment-specifically regenerative treatments. One treatment for joint repair is Prolotherapy. For individuals receiving regenerative treatments like Prolotherapy, motion and exercise are encouraged for their synergistic effects.
DEGENERATIVE CONDITIONS RESPOND TO REGENERATIVE TREATMENTS
Prolotherapy is a regenerative injection technique used to stimulate repair of injured tissue and relieve pain. It works by stimulating proliferation of new tissue at the injection sites, promoting the three stages of healing: inflammation, proliferation and remodeling.
Prolotherapy triggers healing via a local ized inflammation. After Prolotherapy solutions are injected at the injury site, a cellular reaction takes place in which various cells, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells and myofibrolasts, form new blood vessels and ultimately lay down collagen which enhances tissue repair and strength. The collagenous connective tissue produced, is new tissue identical to the collagen fabric of normal connective tissue. The collagen fiber length and alignment are regular, and ligament attachments are stronger.
STEM CELLS ARE ADVANCING JOINT PAIN TREATMENT OPTIONS
The most common and most researched proliferant used in Prolotherapy is dextrose. This attracts healing cells to the damaged joint. When a person has more advanced osteoarthritis, tissue tear, or other severe joint injury, a person’s own stem or healing cells can be added as a proliferant. Blood, bone marrow and/or adipose (fat) tissue are excellent sources for healing cells which can be quickly drawn and re-injected via a comprehensive injection technique for joint repair stimulation. These treatments address the white tissues of the joint, bringing restoring cells directly to the area of cellular deficiency.
S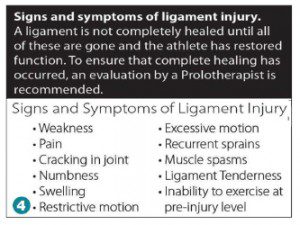 uspect a ligament injury? Some common signs and symptoms of a ligament injury include pain, tenderness, crepitus, inhibited or excessive motion, and others. (See Figure 4.) A Regenerative Medicine specialist can provide a proper evaluation for non-surgical treatment options that can repair the joint, alleviate pain, and allow a person to naturally return to activities and sports, without merely masking the pain.
uspect a ligament injury? Some common signs and symptoms of a ligament injury include pain, tenderness, crepitus, inhibited or excessive motion, and others. (See Figure 4.) A Regenerative Medicine specialist can provide a proper evaluation for non-surgical treatment options that can repair the joint, alleviate pain, and allow a person to naturally return to activities and sports, without merely masking the pain.
PROLOTHERAPY SPECIALISTS:
Ross A. Hauser, MD.
Danielle R. Steilen. MMS, PA-C
Timothy L. Speciale, DO
239-303-4546
www.CaringMedical.com